PINCHA AQUI Y REPASEMOS GRAMÁTICA
PINCHA AQUI, TEST DE TODO
JUEGO DE WHAT, WHERE, WHEN....
VERBOS OPUESTOS, JUEGO
VOCABULARIOS OPUESTOS
SINONIMOS
VERBOS SEGUIDOS DE PREPOSICIONES
JUEGOS
JUEGOS VOCABULARIO SENCILLOS
SOPAS DE LETRAS VOCABULARIO FÁCIL/DIFICIL
CHITES EN INGLÉS
PINCHA AQUI Y HAZ COMPRENSIÓN LECTORA
PINCHA AQUI Y HAZ COMPRENSIÓN LECTORA
COMPRENSIÓN LECTORA Y PREGUNTAS RESP
PINCHA AQUI Y RESPONDE A CUESTIONES SENCILLAS (TEST)
THERE IS/ARE
REPASO INGLÉS TEST
REPASO GRAMÁTICA INGLÉS
ELIGE Y JUEGA
REPASA LOS TIEMPOS VERBALES
MUCHOS JUEGOS DE VOCABULARIO Y COMPRENSIÓN LECTORA EN INGLÉS
JUEGOS DE TODO UN POCO DE REPASO
JUEGOS
REPASO DE TODO PARA 4º
JUEGO PALABRAS RÁPIDO

TEORIA TIEMPOS VERBALES CON SUS MARCADORES
COMPARATIVA TIEMPOS VERBALES
TIPOS DE VERBOS: AUXILIARES, MODALES....



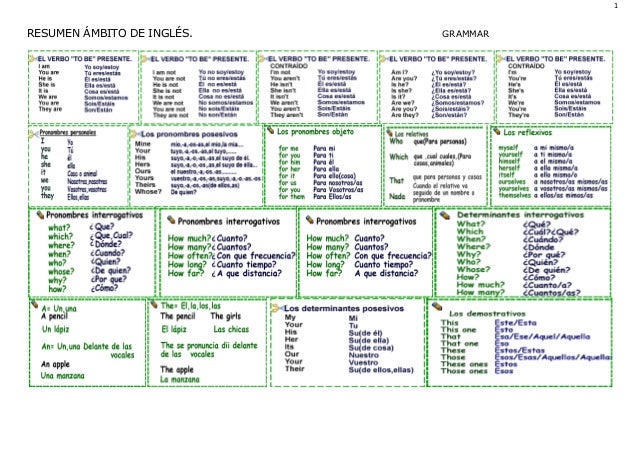





REPASO DE INGLÉS PARA 1º PRIMARIA



VOCABULARIO EN INGLÉS DE CONSULTA

REPASO VOCABULARIO 1º PRIMARIA

VOCABULARIO 1º PRIMARIA

REPASO INGLÉS BÁSICO PARA 4º PRIMARIA PDF
GENERADOR DE VOCABULARIO
Pronombres
Personales |
Pronombres
Acusativos |
Adjetivos
Posesivos |
Pronombres
Posesivos |
Pronombres
Reflexivos |
I
|
me
|
my
|
mine
|
myself
|
you
|
you
|
your
|
yours
|
yourself
|
he
|
him
|
his
|
his
|
himself
|
she
|
her
|
her
|
hers
|
herself
|
it
|
it
|
its
|
--
|
itself
|
we
|
us
|
our
|
ours
|
ourselves
|
you
|
you
|
your
|
yours
|
yourselves
|
they
|
them
|
their
|
theirs
|
themselves
|
Pronombres
Indefinidos
|
||||
everybody
|
nobody
|
somebody
|
anybody
|
|
everyone
|
no one
|
someone
|
anyone
|
|
everything
|
nothing
|
something
|
anything
|
|
Pronombres Relativos
|
||||
who
|
which
|
that
|
whom
|
whose
|
Pronombres Recíprocos
|
||||
each other / one another
|
||||
VERBOS PRINCIPALES
Los verbos en inglés más
importantes son: El verbo "to be", el verbo "to have", los
verbos modales: "can, could, may, might, should, must, ought to" y
los verbos auxiliares: "will" y "would". Aquí encontrarás
ejemplos de esos verbos traducidos al español.
Verbos Primarios
Verbo "to be" - ser
o estarI am / I was / I have been / I had been / I will be / …
Verbo "to have" - haber
o tenerI have / I had / I have had / I had had / I will have / …
Verbos Modales
Can - puedoI can dance.
Could - podría / pude / podía / pudieraI could dance
if I could practice.
May - podría / quizás / puede queIt may rain
today.
Might - podría / quizás / puede queThey might come
tomorrow.
Must - debo / debo deI must go. - She must be
crazy.
Should - debería / tendría queI should study more.
Ought to - debería / tendría queI ought to study more.
Verbos Auxiliares
Will - (convierte en futuro al verbo que le sigue)I
will speak English.
Would - (convierte en potencial al verbo que le sigue)I
would speak English.
1. VERBO “TO BE”
Present
|
Present Perfect
|
I am a
student
Soy un estudiante I am studying Estoy estudiando |
I have been a
student
He sido un estudiante I have been studying He estado estudiando |
Past
|
Past Perfect
|
I was a
student
Fui/era un estudiante I was studying Estuve/estaba estudiando |
I had been a
student
Había sido un estudiante I had been studying Había estado estudiando |
Future
|
Future Perfect
|
I will be a
student
Seré un estudiante I will be studying Estaré estudiando |
I will
have been a
student
Habré sido un estudiante I will have been studying Habré estado estudiando |
Conditional
|
Conditional Perfect
|
I would be a
student
Sería un estudiante I would be studying Estaría estudiando |
I would
have been a
student
Habría sido un estudiante I would have been studying Habría estado estudiando |
Forma Afirmativa
|
Forma Negativa
|
Forma Interrogativa
|
I am (I'm)
|
I am not (I'm not)
|
am I?
|
soy, estoy
|
no soy, no estoy
|
¿soy yo?, ¿estoy yo?
|
you are (you're)
|
you are not (you're
not)
|
are you?
|
eres, estás
|
no eres, no estás
|
¿eres tú?, ¿estás tú?
|
he is (he's)
|
he is not (he's not)
|
is he?
|
él es, está
|
él no es, no está
|
¿es él?, ¿está él?
|
we are (we're)
|
we are not (we're
not)
|
are we?
|
somos, estamos
|
no somos, no estamos
|
¿somos?, ¿estamos?
|
you are (you're)
|
you are not (you're
not)
|
are you?
|
sois, estáis
|
no sois, no estáis
|
¿sois?, ¿estáis?
|
they are (they're)
|
they are not (they're
not)
|
are they?
|
ellos son, están
|
ellos no son, no están
|
¿son, están ellos?
|
Forma Afirmativa
|
Forma Negativa
|
Forma Interrogativa
|
I was
|
I was not (I wasn't)
|
was I?
|
fui, era,
estuve, estaba |
no fui, no era,
no estuve, no estaba |
¿fui?, ¿era?
¿estuve?, ¿estaba? |
you were
|
you were not (you
weren't)
|
were you?
|
fuiste, eras,
estuviste, estabas |
no fuiste, no eras,
no estuviste, no estabas |
¿fuiste?, ¿eras?
¿estuviste?, ¿estabas? |
he was
|
he was not (he
wasn't)
|
was he?
|
fue, era,
estuvo, estaba |
no fue, no era,
no estuvo, no estaba |
¿fue?, ¿era?
¿estuvo?. ¿estaba? |
we were
|
we were not (we
weren't)
|
were we?
|
fuimos, éramos,
estuvimos, estábamos |
no fuimos, no éramos,
no estuvimos, no estábamos |
¿fuimos?, ¿éramos?
¿estuvimos?, ¿estábamos? |
you were
|
you were not (you
weren't)
|
were you?
|
fuisteis, erais,
estuvisteis, estabais |
no fuisteis, no erais,
no estuvisteis, no estabais |
¿fuisteis?, ¿erais?,
¿estuvisteis?, ¿estabais? |
they were
|
they were not (they
weren't)
|
were they?
|
fueron, eran
estuvieron, estaban |
no fueron, no eran,
no estuvieron, no estaban |
¿fueron?, ¿eran?
¿estuvieron?, ¿estaban? |
- VERBO “TO HAVE”
Present
|
Present Perfect
|
I have an
exam
Tengo un examen I have to study Tengo que estudiar |
I have had an
exam
He tenido un examen I have had to study He tenido que estudiar |
Past
|
Past Perfect
|
I had an
exam
Tuve/tenía un examen I had to study Tuve/tenía que estudiar |
I had had an
exam
Había tenido un examen I had had to study Había tenido que estudiar |
Future
|
Future Perfect
|
I will have an
exam
Tendré un examen I will have to study Tendré que estudiar |
I will
have had an
exam
Habré tenido un examen I will have had to study Habré tenido que estudiar |
Conditional
|
Conditional Perfect
|
I would have an
exam
Tendría un examen I would have to study Tendría que estudiar |
I would
have had an
exam
Habría tenido un examen I would have had to study Habría tenido que estudiar |
Forma Afirmativa
(tener)
|
Forma Afirmativa
(haber)
|
I have - yo
tengo
|
I have (I've) - yo he
|
You have - tú
tienes
|
You have (You've) - tú has
|
He has - él
tiene
|
He has (He's) - él ha
|
We have -
nosotros tenemos
|
We have (We've) - nosotros hemos
|
You have -
ustedes tienen
|
You have (You've) - ustedes han
|
They have -
ellos tienen
|
They have (They've) - ellos han
|
Forma Negativa
(tener)
|
Forma Negativa
(haber)
|
I don't have - no tengo
|
I haven't - no
he
|
You don't have - tú no tienes
|
You haven't - tú
no has
|
He doesn't have - él no tiene
|
He hasn't - él
no ha
|
We don't have - nosotros no tenemos
|
We haven't -
nosotros no hemos
|
You don't have - ustedes no tienen
|
You haven't -
ustedes no han
|
They don't have - ellos no tienen
|
They haven't -
ellos no han
|
Forma Interrogativa
(tener)
|
Forma Interrogativa
(haber)
|
Do I have? - ¿tengo yo?
|
Have I? - ¿he yo?
|
Do you have? - ¿tienes tú?
|
Have you? - ¿has tú?
|
Does he have? - ¿tiene él?
|
Has he? - ¿ha él?
|
Do we have? - ¿tenemos nosotros?
|
Have we? - ¿hemos nosotros?
|
Do you have? - ¿tienen ustedes?
|
Have you? - ¿han ustedes?
|
Do they have? - ¿tienen ellos?
|
Have they? - ¿han ellos?
|
- VERBOS MODALES:
- VERBO “CAN”
El verbo 'Can' pertenece a los
verbos modales y se ubica antes del verbo principal en infinitivo. Significa
'poder'. Se utiliza para expresar habilidad, permiso.
I can - puedo
Affirmative
·
·
I can play
the trumpet.
Yo puedo/sé tocar la trompeta.
Yo puedo/sé tocar la trompeta.
·
We can take a
taxi to the airport.
Podemos tomar un taxi hasta el aeropuerto.
Podemos tomar un taxi hasta el aeropuerto.
·
Mary can be
very stubborn sometimes.
Mary puede ser muy terca a veces.
Mary puede ser muy terca a veces.
·
You can sit
here if you like.
Puedes sentarte aquí si quieres.
Puedes sentarte aquí si quieres.
·
It can take
longer than we thought.
(Esto) Puede tardar más de lo que pensábamos.
(Esto) Puede tardar más de lo que pensábamos.
·
Nobody can understand
that.
Nadie puede entender eso.
Nadie puede entender eso.
·
Your decision can change
our lives.
Tu decisión puede cambiarnos la vida.
Tu decisión puede cambiarnos la vida.
Negative
·
·
I can not swim.
No puedo/sé nadar.
No puedo/sé nadar.
·
That cannot be
true.
Eso no puede ser cierto.
Eso no puede ser cierto.
·
You can't tell
me what to do.
No puedes decirme qué hacer
No puedes decirme qué hacer
Interrogative
·
·
Can Peter speak German?
¿Puede/sabe Peter hablar alemán?
¿Puede/sabe Peter hablar alemán?
·
Can you help me with my homework?
¿Me puedes ayudar con mi tarea?
¿Me puedes ayudar con mi tarea?
Can + have
·
·
Paul can have gone
to Maria's.
Paul puede haber ido a lo de María.
Paul puede haber ido a lo de María.
·
They can't have left
without us.
Ellos no pueden haberse ido sin nosotros.
Ellos no pueden haberse ido sin nosotros.
·
Jane can't have said
that.
Jane no puede haber dicho eso.
Jane no puede haber dicho eso.
- VERBO “COULD”
El verbo 'Could' Expresa poca
probabilidad o condicionalidad. Significa: podría, pude, podía, pudiera de
acuerdo con el contexto: I could dance if I could practice.
I could - podría / pude / podía / pudiera
Affirmative
·
·
You could be
wrong.
Podrías estar equivocado.
Podrías estar equivocado.
·
They could manage
without us.
Ellos pudieron/podrían arreglárselas sin nosotros.
Ellos pudieron/podrían arreglárselas sin nosotros.
·
I could help
Ann if she only let me.
Yo podría ayudar a Ann si tan solo me dejara.
Yo podría ayudar a Ann si tan solo me dejara.
·
This new plan could be
very risky.
Este nuevo plan podría ser muy riesgoso.
Este nuevo plan podría ser muy riesgoso.
·
The news could kill
Mr. Taylor.
La noticia podría matarlo al señor Taylor.
La noticia podría matarlo al señor Taylor.
·
Anybody could be
chosen for the job.
Cualquiera podría ser elegido para el trabajo.
Cualquiera podría ser elegido para el trabajo.
·
I could go
back and bring Kate with me.
Yo podría/pude volver y traer a Kate conmigo.
Yo podría/pude volver y traer a Kate conmigo.
Negative
·
·
I couldn't see
very clearly.
Yo no pude/podría ver muy claramente.
Yo no pude/podría ver muy claramente.
·
Mrs. Jones couldn't stand
the smell.
La señora Jones no pudo/podría soportar el olor.
La señora Jones no pudo/podría soportar el olor.
·
We couldn't leave
you alone.
No podríamos dejarte solo.
No podríamos dejarte solo.
Interrogative
·
·
Could you open the window?
¿Pudiste/podrías abrir la ventana?
¿Pudiste/podrías abrir la ventana?
·
Could they escape?
¿Pudieron/podrían escapar?
¿Pudieron/podrían escapar?
Could + have
·
·
You could have told me you weren't at home!
¡Podrías haberme dicho que no estabas en casa!
¡Podrías haberme dicho que no estabas en casa!
·
It could have been worse.
Pudo/podría haber sido peor.
Pudo/podría haber sido peor.
·
John couldn't have done that.
John no pudo/podría haber hecho eso.
John no pudo/podría haber hecho eso.
C. VERBO “MAY”
El verbo 'may' se utiliza para
expresar cierto grado de probabilidad de una acción o grado de certeza: It may
rain today. Significa: podría, quizás, puede que.
I may - podría / quizás / puede que
Affirmative
·
·
We may stay
here for the night.
Podríamos pasar la noche aquí.
Podríamos pasar la noche aquí.
·
Jack may be
telling the truth.
Puede que Jack esté diciendo la verdad.
Puede que Jack esté diciendo la verdad.
·
You may ask
three questions.
Puedes hacer tres preguntas.
Puedes hacer tres preguntas.
·
I may visit
Susan on Monday.
Quizás la visite a Susan el lunes.
Quizás la visite a Susan el lunes.
·
The road may be
blocked.
El camino podría estar bloqueado.
El camino podría estar bloqueado.
·
That may be a
good idea.
(Esa) Quizá sea una buena idea.
(Esa) Quizá sea una buena idea.
·
Carol may go
when she finishes.
Carol puede/podrá ir cuando termine.
Carol puede/podrá ir cuando termine.
Negative
·
·
Mr. Johnson may not remember
anything.
Puede que el señor Johnson no recuerde nada.
Puede que el señor Johnson no recuerde nada.
·
You may not leave
the classroom without permission.
Usted no puede salir del aula sin permiso.
Usted no puede salir del aula sin permiso.
·
I may not come
next week.
Quizá no venga la semana que viene.
Quizá no venga la semana que viene.
Interrogative
·
·
May I go to the bathroom?
¿Puedo ir al baño?
¿Puedo ir al baño?
·
May you take this to Mr. Richards?
¿Podrías llevarle esto al señor Richards?
¿Podrías llevarle esto al señor Richards?
May + have
·
·
Vicky may have told
me.
Puede que Vicky me haya dicho.
Puede que Vicky me haya dicho.
·
They may not have known that.
Puede que ellos no hayan sabido eso.
Puede que ellos no hayan sabido eso.
·
I may have forgotten
to lock the door.
Quizá me haya olvidado de cerrar la puerta con llave.
Quizá me haya olvidado de cerrar la puerta con llave.
- VERBO “MIGTH”
El verbo 'might' expresa débil
probabilidad o posibilidad. Se utiliza cuando queremos decir: podría, quizás,
puede que (They might come tomorrow).
I might - podría / quizás / puede que
Affirmative
·
¡Error! Objeto
incrustado no válido.
·
They might be
waiting for us at the station.
Podrían estar esperándonos en la estación.
Podrían estar esperándonos en la estación.
·
This might be our
only chance
Esta podría ser nuestra única oportunidad.
Esta podría ser nuestra única oportunidad.
·
I might lose
my job.
Podría perder mi trabajo.
Podría perder mi trabajo.
·
Harry might write
soon.
Harry podría escribir pronto.
Harry podría escribir pronto.
·
You might find a
solution.
Podrías encontrar una solución.
Podrías encontrar una solución.
·
We might be
going the wrong way.
Quizás estemos yendo en la dirección equivocada.
Quizás estemos yendo en la dirección equivocada.
·
I might call
you tomorrow.
Podría llamarte mañana.
Podría llamarte mañana.
Negative
·
·
Sylvia might not live
there anymore.
Quizás Sylvia ya no viva más ahí.
Quizás Sylvia ya no viva más ahí.
·
We might not know
everything.
Puede que no sepamos todo.
Puede que no sepamos todo.
·
It might not rain
tonight.
Puede que no llueva esta noche.
Puede que no llueva esta noche.
Interrogative
·
·
Might I give you a piece of advice?
¿Podría darte un consejo?
¿Podría darte un consejo?
·
Might we speak to you for a moment?
¿Podríamos hablar contigo un momento?
¿Podríamos hablar contigo un momento?
Might + have
·
·
They might have finished
earlier.
Quizás hayan terminado más temprano.
Quizás hayan terminado más temprano.
·
Bob might have died
in the accident.
Bob podría haber muerto en el accidente.
Bob podría haber muerto en el accidente.
·
Miss Green might not have been present at the time.
Puede que la señorita Green no haya estado presente en ese momento.
Puede que la señorita Green no haya estado presente en ese momento.
- VERBO “MUST”
El verbo 'must' expresa una
prohibición u obligación fuerte así como cierta certeza: I must go. She must be
crazy. En español significa debo, debo de.
I must - debo / debo de
Affirmative
·
·
I must go to
the library.
Debo ir a la biblioteca.
Debo ir a la biblioteca.
·
You must stay
here until I come back.
Debes quedarte aquí hasta que yo vuelva.
Debes quedarte aquí hasta que yo vuelva.
·
We must be at
the airport at three o'clock.
Debemos estar en el aeropuerto a las tres.
Debemos estar en el aeropuerto a las tres.
·
Everybody must wear a
uniform.
Todos deben usar uniforme.
Todos deben usar uniforme.
·
You must be
joking!
¡Deben de estar bromeando!
¡Deben de estar bromeando!
·
Julia must be in
Paris by now.
Julia ya debe de estar en París.
Julia ya debe de estar en París.
·
It must be
noon already.
Ya debe de ser mediodía.
Ya debe de ser mediodía.
Negative
·
·
You must not talk
to strangers.
No debes hablar con extraños.
No debes hablar con extraños.
·
We mustn't make
noise.
No debemos hacer ruido.
No debemos hacer ruido.
·
Mr. Williams must not smoke.
El señor Williams no debe fumar.
El señor Williams no debe fumar.
Interrogative
·
·
Must we do everything today?
¿Debemos hacer todo hoy?
¿Debemos hacer todo hoy?
·
Must you go so soon?
¿Debes irte tan pronto?
¿Debes irte tan pronto?
Must + have
·
·
I must have fallen
asleep.
Debo de haberme quedado dormido.
Debo de haberme quedado dormido.
·
Sally must have forgotten
about the meeting.
Sally debe de haberse olvidado de la reunión.
Sally debe de haberse olvidado de la reunión.
·
They must have sent
it already.
Ya deben de haberlo enviado.
Ya deben de haberlo enviado.
- VERBO “SHOULD”
Usamos 'should' para expresar
grado de posibilidad o probabilidad, así como también para obligación débil.
Significa: debería, tendría que. I should study.
I should - debería / tendría que
Affirmative
·
·
You should tell
Miss Baker the truth.
Deberías decirle la verdad a la señorita Baker.
Deberías decirle la verdad a la señorita Baker.
·
We should go to
sleep.
Deberíamos ir a dormir.
Deberíamos ir a dormir.
·
I should call
my mother.
Debería llamar a mi madre.
Debería llamar a mi madre.
·
They should leave
as soon as possible.
Ellos deberían salir lo antes posible.
Ellos deberían salir lo antes posible.
·
She should be
doing her homework.
Ella debería estar haciendo su tarea.
Ella debería estar haciendo su tarea.
·
Ben should exercise
more.
Ben debería ejercitarse más.
Ben debería ejercitarse más.
·
It should be
here.
(Esto) Debería estar aquí.
(Esto) Debería estar aquí.
Negative
·
·
You should not say
that.
No deberías decir eso.
No deberías decir eso.
·
Nick shouldn't be
working.
Nick no debería estar trabajando.
Nick no debería estar trabajando.
·
It shouldn't take
long.
(Esto) No debería tardar mucho.
(Esto) No debería tardar mucho.
Interrogative
·
·
Should I write Maggie a letter?
¿Debería yo escribirle una carta a Maggie?
¿Debería yo escribirle una carta a Maggie?
·
Should we worry?
¿Deberíamos preocuparnos?
¿Deberíamos preocuparnos?
Should + have
·
·
Charlie should have consulted me.
Charlie debería haberme consultado.
Charlie debería haberme consultado.
·
I shouldn't have eaten so much.
Yo no debería haber comido tanto.
Yo no debería haber comido tanto.
·
Danny and Paul should have waited for you.
Danny y Paul deberían haberte esperado.
Danny y Paul deberían haberte esperado.
- VERBO “OUGTH”
El verbo 'ought to' es igual
al 'should' y expresa una obligación débil. Significa debería, tendría que.
I ought
to - debería / tendría que
Affirmative
·
·
Helen ought to be
more careful.
Helen debería tener más cuidado.
Helen debería tener más cuidado.
·
I ought to stay
in bed.
Yo debería quedarme en la cama.
Yo debería quedarme en la cama.
·
We ought to go
together.
Deberíamos ir juntos.
Deberíamos ir juntos.
·
They ought to be
here already.
Ellos ya deberían estar aquí.
Ellos ya deberían estar aquí.
·
You ought to eat
more vegetables.
Deberías comer más vegetales.
Deberías comer más vegetales.
·
Tom ought to take
her home.
Tom debería llevarla a casa.
Tom debería llevarla a casa.
·
It ought to work
properly.
(Esto) Debería funcionar correctamente.
(Esto) Debería funcionar correctamente.
Negative
·
·
You ought not to drink so much.
No deberías beber tanto.
No deberías beber tanto.
·
They ought not to go camping without a torch.
Ellos no deberían ir de camping sin una linterna.
Ellos no deberían ir de camping sin una linterna.
·
George ought not to wear someone else's glasses.
George no debería usar los anteojos de otra persona.
George no debería usar los anteojos de otra persona.
Interrogative
·
·
Ought Rachel to be
here so early?
¿Debería Rachel estar aquí tan temprano?
¿Debería Rachel estar aquí tan temprano?
·
Ought they to live
there?
¿Deberían ellos vivir allí?
¿Deberían ellos vivir allí?
Ought to + have
·
·
You ought to have read the book for today.
Deberían haber leído el libro para hoy.
Deberían haber leído el libro para hoy.
·
They ought to have gone to the supermarket.
Ellos deberían haber ido al supermercado.
Ellos deberían haber ido al supermercado.
·
We ought to have listened to the guard.
Deberíamos haber escuchado al guardia.
Deberíamos haber escuchado al guardia.
- VERBOS AUXILIARES:
- VERBO “WILL”
En inglés no existen los
verbos en futuro, sino que al agregar will, convertimos en futuro al verbo que
le sigue: I will come to see you tonight.
I will go - iré
I will eat - comeré
I will be - seré / estaré
I will have - tendré / habré
I will eat - comeré
I will be - seré / estaré
I will have - tendré / habré
Affirmative
·
·
Bill will finish
this later.
Bill terminará esto después.
Bill terminará esto después.
·
This will be very
easy.
Esto será muy fácil.
Esto será muy fácil.
·
I will call
you back.
Yo te volveré a llamar.
Yo te volveré a llamar.
·
It will rain
next week.
Lloverá la semana que viene.
Lloverá la semana que viene.
·
They will catch
you if you stay.
Te atraparán si te quedas.
Te atraparán si te quedas.
·
We will go
there the day after tomorrow.
Iremos allí pasado mañana.
Iremos allí pasado mañana.
·
You will get
lost in the city.
Te perderás en la ciudad.
Te perderás en la ciudad.
Negative
·
·
I won't sleep
tonight.
No dormiré esta noche.
No dormiré esta noche.
·
They will not come.
Ellos no vendrán.
Ellos no vendrán.
·
You won't like
it.
No te gustará.
No te gustará.
Interrogative
·
·
Will Mrs. Lennon understand me?
¿La señora Lennon me entenderá?
¿La señora Lennon me entenderá?
·
Will you take me with you?
¿Me llevarás contigo?
¿Me llevarás contigo?
Will + have
·
·
Mr. Philips will have left
by this evening.
El señor Philips se habrá ido esta noche.
El señor Philips se habrá ido esta noche.
·
I will have finished
the book by tomorrow.
Habré terminado el libro mañana.
Habré terminado el libro mañana.
·
We will have eaten
everything by next week.
Nos habremos comido todo la semana que viene.
Nos habremos comido todo la semana que viene.
- VERBO “WOULD”
'Would' es el pasado de will
en algunos casos y verbo auxiliar en otros. Convierte en potencial al verbo que
le sigue y va seguido del verbo en forma base.
I would go - iría
I would eat - comería
I would be - sería / estaría
I would have - tendría / habría
I would eat - comería
I would be - sería / estaría
I would have - tendría / habría
Affirmative
·
·
I would go to
the party.
Yo iría a la fiesta.
Yo iría a la fiesta.
·
You would feel
better.
Te sentirías mejor.
Te sentirías mejor.
·
That would be
great.
Eso sería genial.
Eso sería genial.
·
We would help
you.
Nosotros te ayudaríamos.
Nosotros te ayudaríamos.
·
Joan would start
to cry.
Joan comenzaría a llorar.
Joan comenzaría a llorar.
·
Glenn would come
right away.
Glenn vendría enseguida.
Glenn vendría enseguida.
·
They would get
very angry.
Ellos se enojarían mucho.
Ellos se enojarían mucho.
Negative
·
·
She would not be
happy.
Ella no sería feliz.
Ella no sería feliz.
·
We wouldn't spend
all the money.
No gastaríamos todo el dinero.
No gastaríamos todo el dinero.
·
I wouldn't do
that.
Yo no haría eso.
Yo no haría eso.
Interrogative
·
·
Would he give Patty a diamond ring?
¿Él le daría a Patty un anillo de diamantes?
¿Él le daría a Patty un anillo de diamantes?
·
Would you mind?
¿Te importaría?
¿Te importaría?







No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario